7 Causes Of Procrastination: Stop Putting Things Off!
Are you constantly putting things off, feeling overwhelmed by tasks, and struggling to get things done? Procrastination is a pervasive issue, affecting people from all walks of life, but understanding its root causes is the first step towards breaking free from its grip and reclaiming control of your time and productivity.
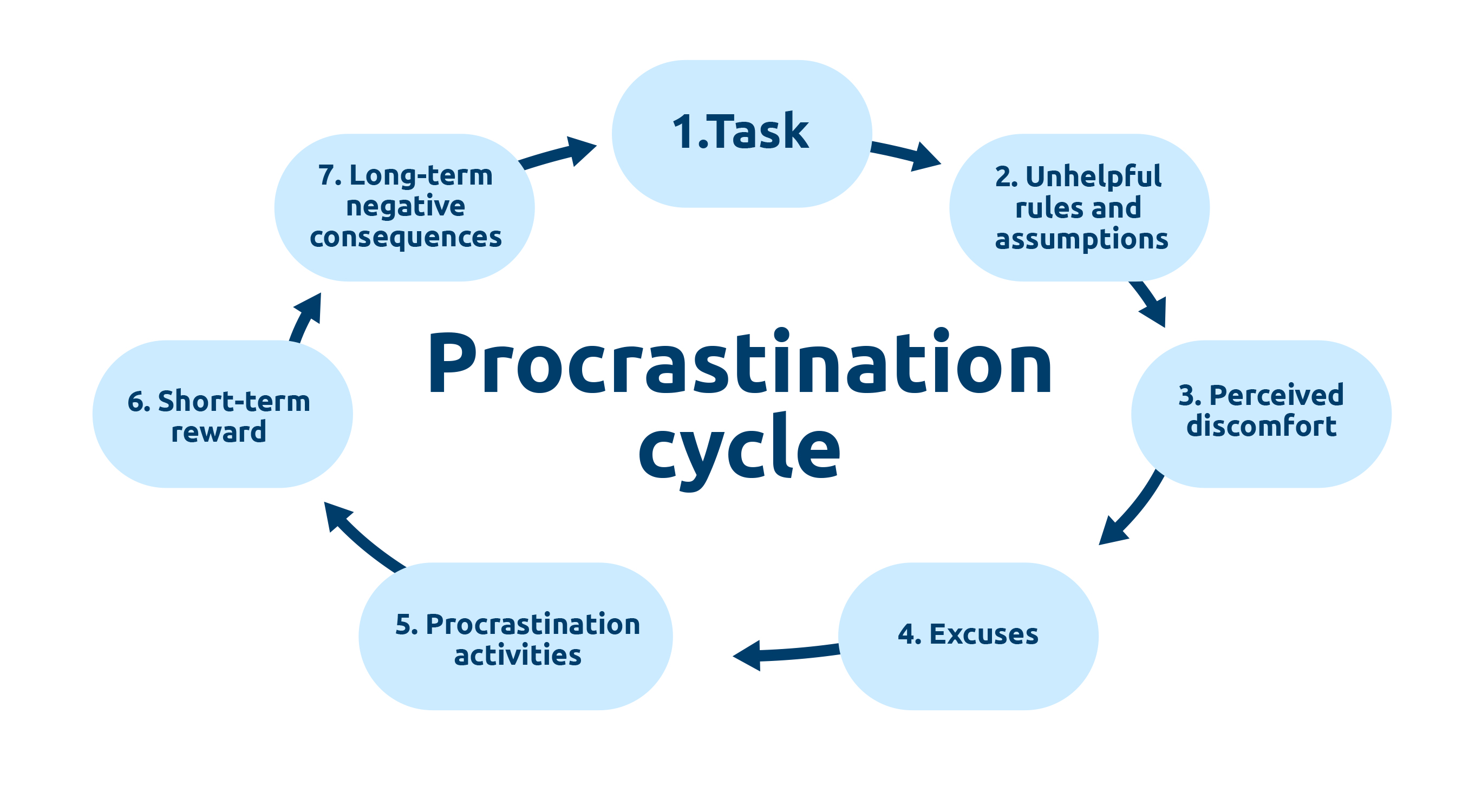
Procrastination, at its core, is the act of delaying or postponing tasks, often until the last minute or past their deadline. While it may seem like a simple act of laziness, the reality is far more complex. "All procrastination is delay, but not all delay is procrastination," as researchers in the field often explain. It's a very specific type of delay, driven by a variety of underlying factors.
Procrastination affects students, professionals, and everyone in between. Whether it's a work project, a personal goal, or a simple chore, the tendency to delay can lead to stress, missed deadlines, and a sense of inadequacy. The good news is that by exploring the reasons behind procrastination and adopting effective strategies, it is possible to overcome this often debilitating habit.
Let's delve into some of the common issues at the heart of chronic procrastination. By pinpointing these root causes, we can develop solutions and strategies to transform our approach to work and life. It's about creating the life you want by taking control of your time and actions.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Cause | Fear of Failure, Perfectionism, Poor Time Management, Lack of Motivation, Fear of Success, Poor Emotional Regulation, Task Aversiveness |
| Description | Individuals may put off tasks due to a fear of not meeting expectations, a desire for flawless results leading to avoidance, inability to prioritize tasks, a lack of interest or perceived importance, the apprehension of increased responsibility, difficulty managing emotions associated with tasks, or the general unpleasantness of a task. |
| Impact | Increased stress, decreased productivity, missed deadlines, lower grades (for students), potential negative impact on career, reduced overall well-being, feelings of guilt and shame. |
| Solutions | Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Focus on progress, not perfection. Use time management techniques like the Pomodoro Technique or time blocking. Identify and address the underlying lack of motivation. Set realistic goals. Develop strategies to manage emotions related to task. Seek professional help from therapist. |
| Additional Points | Procrastination is a complex behavior with various factors. The costs of procrastination can be considerable, leading to physical, emotional, and practical consequences. It's not simply laziness, but can be related to mental health challenges, such as ADHD or anxiety. Understanding personal triggers is key to developing effective strategies. Time management is crucial in overcoming procrastination. |
| Examples | A student putting off studying for an exam, an employee delaying a report, someone postponing a doctor's appointment or avoiding paying bills. |
| Reference |
Procrastination isn't always about laziness. It's frequently a symptom of underlying issues, such as low priorities, fear of failure, or poor emotional regulation. It's crucial to recognize that procrastination can be linked to mental health challenges. Though not a mental illness itself, it's connected to conditions such as ADHD and anxiety. This understanding allows us to approach the problem with compassion and develop targeted strategies.
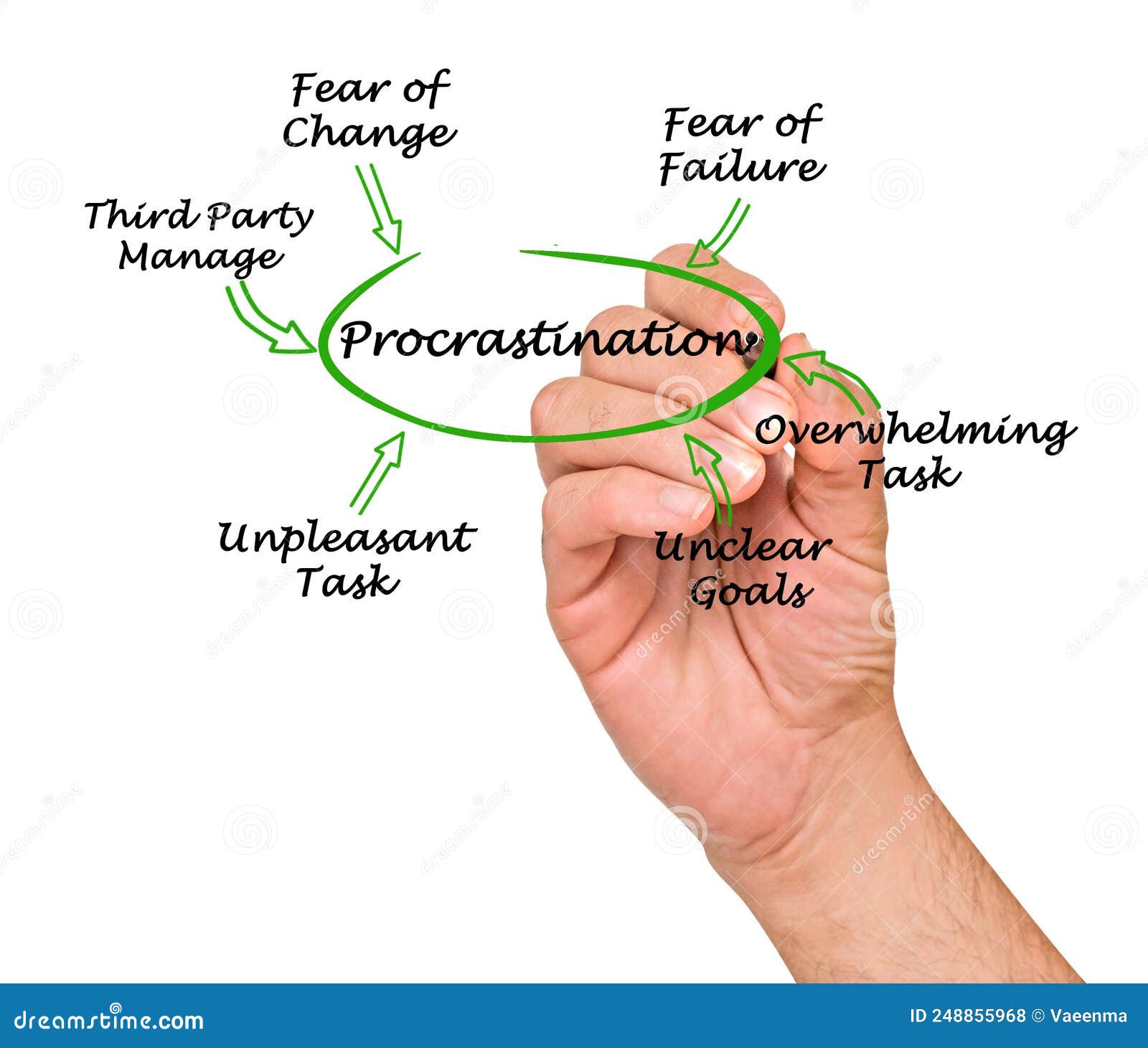
One common cause is perfectionism. The desire for flawless results can paralyze individuals, leading them to avoid starting a task altogether. Fear of failure is another significant driver. The thought of not measuring up to expectations can be overwhelming, making procrastination a way to avoid potential disappointment.
Poor time management is another significant contributor. When tasks are not properly prioritized or when there's a lack of effective planning, it's easy to feel overwhelmed and put things off. Understanding your personal triggers is key to developing effective strategies. For instance, if you find that certain environments or distractions make you more prone to procrastination, you can take steps to minimize those influences.
Lack of motivation plays a critical role. If a task doesn't seem important or interesting, it's naturally harder to get started. The avoidance of a task often involves choosing more pleasurable alternatives. This is especially true for students, for whom procrastination can seriously impact grades and overall well-being. The same goes for professionals, where "passive procrastination" can silently undermine career progress.
Procrastination's influence can be traced to a bias that makes it difficult for us to fully appreciate the future consequences of our current actions. This bias often leads to putting things off for immediate gratification, which can have severe consequences.
Understanding the root causes of procrastination is the first step toward breaking free. There are multiple reasons why people procrastinate. Often, they combine different procrastination causes. It's about identifying your personal reasons and taking corresponding action. This personalized approach is the key to effective change.
Let's explore several common roots of procrastination, starting with fear of failure and perfectionism. The quest for flawlessness can paralyze you. The result is avoidance. Overcoming this involves breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps. The focus shifts from perfection to progress.
Another cause involves managing time. Procrastination often stems from a lack of effective time management or an inability to prioritize tasks based on their urgency. This leads to issues with timely task completion. Effective strategies include the Pomodoro Technique, time blocking, and prioritizing tasks. Learning how to manage time is crucial. It is fundamental to overcoming procrastination.
Lack of motivation is a powerful driver of procrastination. If you do not possess the motivation, or the sense of importance, to complete a task, the chances of delaying it increase. This highlights the importance of finding ways to make tasks more engaging and meaningful. It might be about reframing how you look at the task.
Procrastination has a significant impact on well-being. It can trigger considerable emotional, physical, and practical costs. These include higher stress levels, diminished productivity, missed deadlines, and feelings of guilt. Students who routinely procrastinate tend to get lower grades, while workers may face the consequences of "passive procrastination" in the workplace.
In summary, procrastination is complex. Its causes vary, and its effects are far-reaching. It's essential to identify your personal triggers, develop customized solutions, and consistently apply those strategies. It's a journey that requires self-awareness, discipline, and a commitment to change.
The costs of procrastination are substantial. Whether it's putting off a work task, delaying that important phone call, or avoiding the start of a major project, the consequences can be felt in various areas of life. It's about recognizing that "procrastination is the voluntary and unnecessary postponement of important" tasks and taking steps to overcome the urge to delay.
Finally, remember that overcoming procrastination is a process. It's challenging to change stubborn habits. Start by addressing the problem directly. The key to lasting change is not just understanding the causes but also implementing tactics that address the behavior directly. This requires a combination of self-awareness, targeted interventions, and a commitment to consistent effort. The rewards are significant: greater success, enhanced fulfillment, and a stronger sense of personal growth in all aspects of life.